In air break circuit breaker the arc is initiated and extinguish in substantially static air in which the arc moves. Such breakers are used for low voltages, generally up to 15KV and rupturing capacities of 500MVA. Air circuit breaker has several advantages over the oil, as an arc quenching medium. These are
- Elimination of risk and maintenance associated with the use of oil.
- The absence of mechanical stress that is set up by gas pressure and oil movement.
- Elimination of the cost of regular oil replacement that arises due to deterioration of oil with the successive breaking operation.
In the air break, circuit breaker the contact separation and arc extinction take place in air at atmospheric pressure. In air break circuit breaker high resistance principle is employed. In this circuit breaker arc is expanded by the mean of arc runners, arc chutes, and arc resistance is increased by splitting, cooling and lengthening.
The arc resistance is increased to such an extent that the voltage drop across the arc becomes more than the system voltage, and the arc gets extinguished at the current zero of AC wave.
Air break circuit breakers are employed in DC circuits and Ac circuits up to 12,000 voltages. Such breakers are usually of indoor type and installed on vertical panels or indoor draw out switch gear. AC circuit breakers are widely employed indoor medium voltage and low voltage switchgear.
Plain Break Type Air Break Circuit Breaker
It is the simplest one in which contacts are made in the shape of two horns. The air initially strikes across the shortest distance between the horns and is driven steadily upwards by the convection currents caused by heating of air during arcing and the interaction of the magnetic and the electric fields. The arc extends from one tip to the other when the horns are fully separated resulting in lengthening and cooling arc.
The relative slowness of the process and the possibility of arc spreading of adjacent metal works limits the application of about 500V and too low power circuits.
Magnetic Blow-Out Type Air Break Circuit Breaker
Some air circuit breakers are used in the circuits having voltage up to 11 KV, the arc extinction is accomplished using magnetic field provided by the current in blowout coils connected in series with the circuit being interrupted. Such coils are called blow out the coil. The magnetic field itself does not extinguish the arc. It simply moves the arc into chutes where the arc is lengthened, cooled and extinguished. The arc shields prevent arc spreading to an adjacent network.
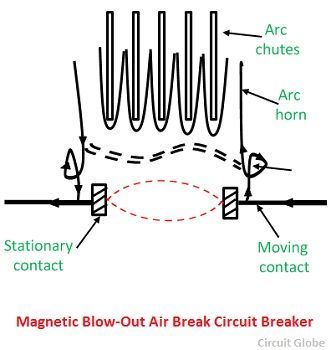 It is important to connect the coils at correct polarity so that the arc is directed upwards. As the breaking action becomes more effective with large currents, this principle has resulted in increasing the rupturing capacities of such breakers to higher values.
It is important to connect the coils at correct polarity so that the arc is directed upwards. As the breaking action becomes more effective with large currents, this principle has resulted in increasing the rupturing capacities of such breakers to higher values.
Arc chute is an efficient device for arc extinction in air and performs the following three interrelated functions
- It confines the arc within a restricted space.
- It provides magnetic control over the arc movement so as to make arc extinction within the devices.
- It provides for the rapid cooling of arc gasses to ensures arc extinction by deionization.
Air Chute Air Break Circuit Breaker
The normal arrangement of air-chute air break circuit breaker employed for low and medium voltage circuits is shown in the figure below. There are two sets of contacts called the main contacts and arcing or auxiliary contacts. Main contacts are usually of copper and conduct the current in the closed position of the breakers. They have low contact resistance and are silver plated.
The arcing contacts are hard, heat resistant and usually of copper alloy. Arcing contacts are used to relieve the main contacts from damage due to arcing. The arcing contacts are easily renewable when required. The auxiliary and arcing contacts close before and open after the main contacts during the operation.
Here the blowouts consist of a steel insert in the arcing chutes. These are so arranged that the magnetic field induced in them by the current in the arc moves it upwards still faster. The steel plates divide the arc into a number of arcs in the series.
The distribution of voltage along the arc length is not linear, but it is accompanied by a rather large anode and cathode drops. In case the total sum of anode and drops of all the short arcs in series exceeds the system voltage, conditions for the quick extinction of the arc are automatically established.
When the contact has come in contact with the relatively cool surfaces of the steel plants gets rapidly and effectively cooled. The movement of the arc may be naturally or aided by a magnetic blowout. Thus, the arc is extinguished by lightening and increasing the power loss of the arc.
Working Principle Air Break Circuit Breaker
When the fault occurs, the main contacts are separate first, and the current is shifted to the arcing contacts. Now the arcing contacts are separate, and the arc is drawn between them. This arc is forced upwards by the electromagnetic forces and thermal action. The arc ends travel along the arc runner. The arc moves upward and is split by the arc splitter plates. The arc is extinguished by lengthening, cooling, splitting, etc.
Applications of Air Break Circuit Breaker
Air break circuit breaker is suitable for the control of power station auxiliaries and industrial plants. They do not require any additional equipment such as compressors, etc. They are mainly used in a place where there are possibilities of fire or explosion hazards. Air break principle of lengthening of the arc, arc runners magnetic blow-up is employed for DC circuit breakers up to 15 KV.
Drawback of Air Break Circuit Breaker
A drawback of arc chute principle is its inefficiency at low currents where the electromagnetic fields are weak. The chute itself is not necessarily less efficient in its lengthening and deionizing action than at high currents, but the arc movement into the chute tends to become slower, and high-speed interruption is not necessarily obtained

What are types of Air break circuit?