There are several differences between the autotransformer and the conventional transformer. One of the major difference between them is that the autotransformer has only one winding whereas the conventional transformer has two separate windings. The other differences between them are explained below in the form of the comparison chart.
Content: Autotransformer V/S Conventional Transformer
Comparison Chart
Definition of Autotransformer
A transformer, having only one winding a part of which acts as a primary winding and the other as secondary is called an autotransformer. The windings of the autotransformer are connected magnetically and electrically.
When the primary voltage is greater than the secondary voltage, then the transformer is called step down autotransformer, and when the primary voltage is smaller than secondary, then it is called step-up auto-transformer.

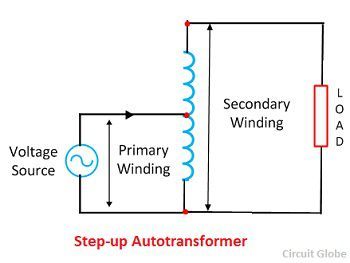 The autotransformer has a low cost, better regulation and low losses. The disadvantage of the autotransformer is that the primary winding of the auto-transformer is not insulated from the secondary. Thus, if the low voltage is supplied from the high voltage, then the full voltage came across the secondary terminal which is dangerous for the load and operator.
The autotransformer has a low cost, better regulation and low losses. The disadvantage of the autotransformer is that the primary winding of the auto-transformer is not insulated from the secondary. Thus, if the low voltage is supplied from the high voltage, then the full voltage came across the secondary terminal which is dangerous for the load and operator.
The auto-transformer is not used for interconnecting the high voltage and low voltage system. It is used in the places where slight variation is required
.
Definition of Conventional Transformer
A conventional transformer is a static device which transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another at the same frequency but different voltage. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, i.e., the electromotive force is induced in the closed circuit due to the variable magnetic field around it. The windings of the conventional transformer are electrically insulated, but magnetically connected.
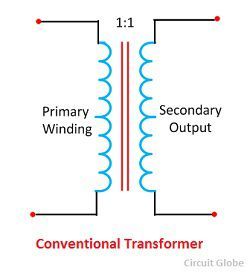 The conventional transformer has two windings. i.e., the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding takes the input from the supply, and the secondary winding is connected to a load and supply energy to the load.
The conventional transformer has two windings. i.e., the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding takes the input from the supply, and the secondary winding is connected to a load and supply energy to the load.
When the output voltage of the transformer is greater than the input voltage, then such type of transformers is called step up transformer, and when the output voltage is less than the input voltage, then it is called a step-down transformer. A transformer in which receiving voltage and the sending voltage is same, then such type of transformer is called one to one transformer.
Key Differences Between Autotransformer and Transformer
- An autotransformer has only one winding which acts both as a primary and the secondary whereas the conventional transformer has a two separate windings, i.e., the primary and the secondary winding.
- The auto-transformer works on the principle of self-induction i.e. induce the electromagnetic force in the circuit due to variation in current. The conventional transformer works on the principle of mutual induction in which the emf induces in the coil by changing the current in the adjacent coil.
- The auto-transformer is smaller in size, whereas the conventional transformer is larger in size.
- The autotransformer is more economical as compared to a conventional transformer.
- In an autotransformer, electrical power is transferred from primary to secondary partly by the process of transformation and partly by the direct current. The conventional transformer transfers the electrical power through the electric transformation due to which power loss occurs.
- The voltage regulation of an auto-transformer is much better than the conventional transformer
- The voltage regulation is the change in the secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load.
- The autotransformer has only one winding. Thus, less conductor is required for winding as compared to the conventional transformer.
- The primary and secondary windings of the autotransformer are not electrically insulated whereas the windings of the conventional transformer are electrically insulated from each other.
- The starting current of the auto-transformer is less than the actual current, whereas the starting current of the conventional transformer is one-third of the main current.
- The auto-transformer is more efficient as compared to the conventional transformer.
- The leakage flux and resistance of an auto-transformer are low because it has only one winding whereas it is high in the conventional transformer.
- The autotransformer has less impedance as compared to conventional current. The smaller impedance results in the large short circuit current.
- The cost of the autotransformer is very less whereas the conventional current is very costly.
- The losses in the auto-transformer are less as compared to the conventional transformer.
- The output voltage of the secondary transformer varies when the sliding contacts are used in the secondary winding whereas the output voltage of the conventional transformer always remains constant.
- The autotransformer is used as a voltage regulator, in the laboratory, in the railway stations, as a stator in an induction motor, etc., whereas the conventional transformer is used to step-up and step-down the voltage in the power grid.
Similarities: The autotransformer and the conventional transformer both work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They used copper conductor for making the windings. The cores of both the transformers are made up of CRGO steel. The primary and the secondary of both the transforms are magnetically connected to each other.


