Definition: Electrostatic deflection is the method of aligning the path of charged particles by applying the electric field between the deflecting plates. The word electrostatic means the strength and the direction of the field changes concerning time. So that, the particles will move only in one direction.
The cathode ray tube uses deflecting plates for modifying the path of electrons. The electrons after exiting through the electron gun pass through deflecting plates. The CRT uses vertical and horizontal plates for focussing the electron beam.
The vertical plate produces an electrical field in the horizontal plane and causes horizontal deflection. The other pair is mounted horizontally and generates an electric field in the vertical plane and causes vertical deflection. These plates allow the beam to pass through the deflecting plates without striking them.
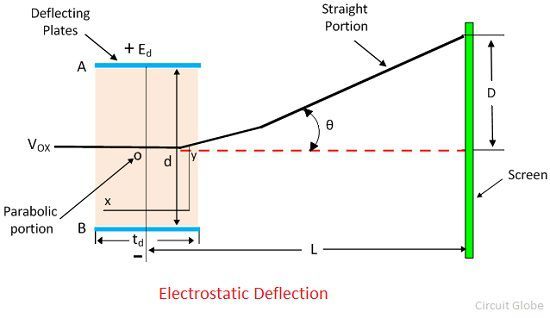
Electrostatic Deflection Arrangement
The general arrangement of the electrostatic deflection is shown in the figure below. The A and B are the two parallel plates between which the potential difference is applied. These deflection plates produce the uniform electrostatic field in the Y direction.
The electron enters between the plates experienced the force only in the Y direction, and the electron will move only in that direction. There is no force either in X direction or the Z direction. Hence, no acceleration of electrons occurs in that direction.
E0 = Voltage of pre-accelerating anode in volt.
e = charge of an electron in coulomb.
m = mass of electron in Kg.
VOX = velocity of the electron when entering into the deflecting plates in meter per second.
Ed = potential between deflecting plates in Volts.
d = distance between deflecting plate in the meter.
Ld = length of deflecting plate in meters.
L = Distance between screen and the mid of the deflecting plates.
D = deflection of the electron beam on the screen in the Y direction.
When the electron moves from the accelerating cathode to anode, they lose their potential energy. The formula gives the potential energy of the electron.
The electrons gain the kinetic energy. And their energy is given by the equation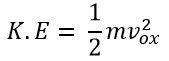
Equating the potential and kinetic energy we get the velocity of the electron when it enters in the deflecting plates.
The velocity of the electron in X direction remains same throughout the deflection plate because no force was acting in the X direction. 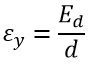
The equation gives the electric field intensity in the Y direction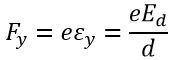
The force acting on the electron in the Y direction. The term ay shows the acceleration of electrons in the y direction.
The initial velocity of the electron enters into the deflection plate is equal to zero, and the equation gives the displacement of an electron in the Y direction at any time t
The velocity in the Y direction is constant, and the displacement in the Y direction is given as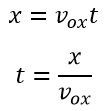
Substituting the value of t in the displacement equation y gives
The above equation represents parabola.The slope at any point is given as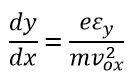
By substituting the x = ld, we get the value of tanθ.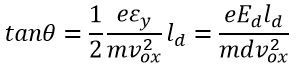
After passing through the deflection plate, the electrons move into the straight line.This straight line is the tangent to the parabola at x = ld and intersect the X-axis at point O’.The equation gives the location of the point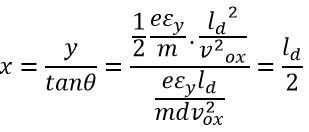
The deflection D on the screen is expressed as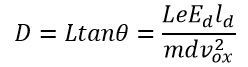
By substituting the value of v2ox in the above equation we get
From the above equation, we can conclude that the deflection of the electron is directly proportional to the deflecting voltage.

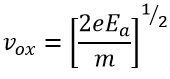
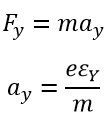
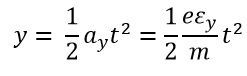
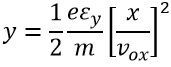
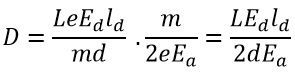
What is Ea? it is not defined in the chart unless it is supposed to be E0 and it is just a typo.
How is Electrostatic deflection in CRT is achieved by a sawtooth waveform?
Request for explanation
Thanks