Definition: A semiconductor device that generates coherent light of high intensity is known as laser diode. LASER is an abbreviation for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Stimulated emission is the basis of working of a laser diode.
Laser diode is similar to LED, however, different from LED, the PN junction of laser diode produces coherent radiation. Coherent radiation means the light waves generated by the device have the same frequency and phase.
Construction of laser diode
The figure below shows the basic construction of a laser diode: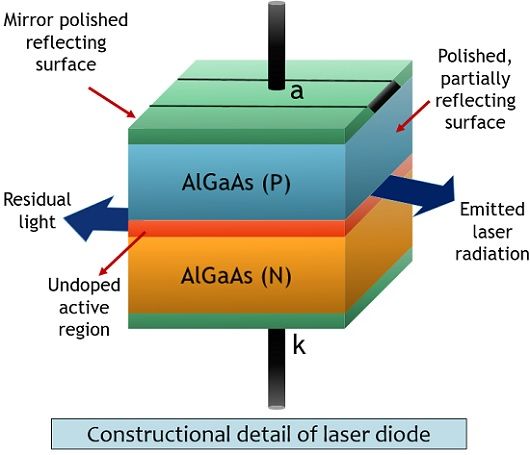
It is formed by doping aluminium or silicon to gallium arsenide material in order to generate n-type and p-type layer. Along with this, an additional active layer of undoped GaAs is placed between the two layers.
The thickness of this active layer is of few nanometers. The aim of sandwiching this layer in between p and n-type layers is to increase the area of electron and hole combination. Resultantly increasing the emitted radiation. The laser output is taken from active region of the laser diode.
In laser diodes, polishing at the two ends of the junction is done in order to provide a mirror-like surface. Through reflection from this surface, more electron and hole pair gets produced. Resultantly that produces more radiation through the device.
Working of laser diode
The working of a laser diode involves 3 processes: absorption, spontaneous emission and stimulated emission.
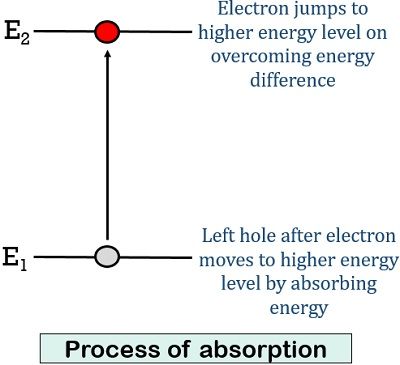
Let us first understand the process of absorption.
Consider 2 energy levels E1 and E2. For simplicity let us assume E1 is the lower energy level and E2 is the higher energy level.
Initially, it is assumed that the atom is in the lower energy state i.e., E1. In order to have transition from a lower energy level to a higher one, the atom requires to overcome the energy difference between the two levels, given by, E2 – E1.
So, some external stimulus is provided to the atom present in the ground state. Thus, an electromagnetic wave of frequency ν is provided to the atom at the ground level. This wave provides sufficient energy to the electron to compensate the energy difference and have transition from E1 to E2. This process is known as absorption.
Moving further now understand the process of spontaneous emission.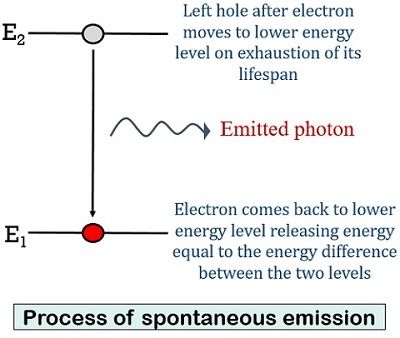
Due to absorption, the atom is present in the energy level E2. So, as the lifespan of the atom expires it now comes back to ground level from the higher energy level. On coming back to ground level the atom emits the energy difference of the two energy levels i.e., E2 – E1.
This energy is emitted by the atom in the form of electromagnetic wave, generating a photon of energy. This process is termed spontaneous emission.
This radiation emission phenomenon is usually seen in optoelectronic devices such as LED.
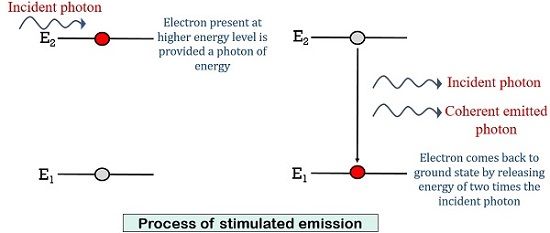
Let us now understand the process of stimulated emission
Suppose after absorption, the atom is present in the higher energy level before the exhaustion of its lifespan. So, an electromagnetic wave of frequency equal to the frequency of spontaneously emitted atom is provided to the atom.
This causes the atom to perform a transition from E2 to E1. Now, this time the atom will release the energy of two photons in this transition.
As we have incorporated the whole junction assembly with a partially reflecting mirror. Thus, this will cause back and forth movement of the atom. Resultantly, this will generate more photons.
As soon as the threshold is achieved, photons will get escaped from the mirror surface, a bright coherent radiation is emitted by the device.
As at the time of stimulated emission we are providing a photon energy to the atom. So, the emitted photons will be in the same phase with the incident photons. Thus, generating a monochromatic bright light.
Characteristics of laser diode
The figure below shows the characteristic curve of a laser diode: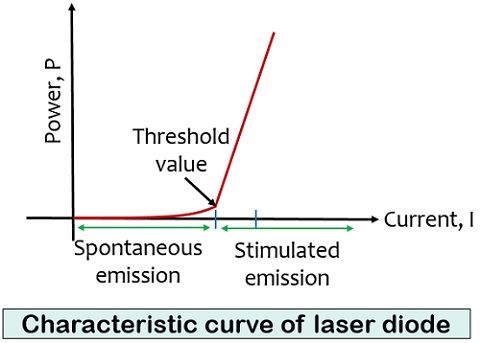
Here, horizontal line denotes current and vertical line shows the optical power of light produced. It can be clearly seen from the figure that a gradual increase in power is noticed until a threshold point is reached.
After the threshold value, a rapid increase in power is noticed even for a small increase in the current. The power produced by the laser diode also depends on the temperature associated with the device.
Property of laser light
A laser light emitted by a laser diode holds the following property:
- Coherence: It is a crucial property of laser, that exists due to stimulated emission. It simply denotes that the wavelength of the waves of emitted light is in phase. When we talk about the ordinary light source for example LED, then it does not show the property of coherence because it gets generated due to the process of spontaneous emission of a photon.
- Monochromaticity: A light emitted by the laser diode is monochrome in nature that means that it has a single wavelength. Waves having single wavelength denotes that the emitted radiation is of a single colour.
- Brightness: Brightness of a light is basically determined by the power per unit surface area per unit solid angle. Due to continuous reflections, a light of high intensity and more power is produced by the laser diode. That resultantly allows the generation of bright light through the device.
- Directionality: A laser light is highly directional this means that the light emitted by a laser diode does not show much divergence. Directionality in a laser diode is achieved because the emitted photons undergo multiple reflections through the mirror. Any time the light deviates from its axis it gets skipped. Thus only a highly focused light beam is achieved.
Advantages of laser diode
- The operational power in case of laser diodes is less as compared to other light emitting devices.
- It is small in size thus allows better handling.
- Laser diodes generate light of high efficiency.
Disadvantages of laser diode
- As it provides a light of high density, thus sometimes puts adverse effects on eyes.
- It is expensive.
Applications of laser diode
Laser diodes are widely used in telecommunication and in defence industries. Optical fiber communication also uses a laser beam for signal transmission as optical fibers requires highly focused beam. It is highly used in laser printers also.