Fuse is a current interrupting device which breaks or opens the circuit by fusing the element when the current in the circuit exceeds a certain value. Fuses are mainly categorised into two types, i.e., High voltage fuses and Low voltage fuses. Low voltage fuses can further divide into two types, namely semi-enclosed or rewirable type and entirely enclosed cartridge type.
Rewirable Fuses
Rewirable fuses are most commonly used in housing wiring and small current circuits. It is also known as a kit – kat fuse. It has a porcelain base which is carrying the fixed contact through which the live wires are connected. The fuse carrier is the independent part which is easily removed or stuck in the base.
The fuse element is made of lead, tin, copper or alloy of tin-lead. The current required for melting the fusing element is twice the value of normal operating current. If more than two or three fuse elements are used in the fuse, then they should be kept away from each other. The de-rating factor of the fuse element is 0.7 to 0.8. When the fault occurs, the fuse element is melt, and the circuit is interrupted.
The melting fuse element takes out of the fuse, and the new one replaces it. The supply is continuous by reinserting the fuse in the base. The rewirable fuse has the advantages of replacement of fuse element without any risk. The cost of the replacement is also very less.
The following are the disadvantages of the rewirable fuse.
Unreliable Operation – For the working of the fuse it is essential to choose the element of suitable size. The element becomes decay because of the oxidation. The oxidation occurs because of the continuous heating of the element.
Low rupturing capacity – The breaking capacity of the fuse is limited. For example, the 2kA is the breaking capacity of the fuse whose normal current capacity is 16A. And fuse whose normal current capacity is 200A, their breaking capacity is 4kA.
Slow Speed of Operation – The arcing time of the fuse is very high. And no additional source is used for extinction the arc.
The risk of Flame and Fire – Because of the rewirable facility the cheap wire is used for the protection of the devices against the short circuit and overload.
Enclosed or Cartridge Type Fuses
The fuse element is enclosed in a closed container. Inside the closed container the fuse element is held by the metal contacts. The fuses are further classified as D-types and link type. Link type cartridge fuses are again of two type viz., knife blade or bolted.
D-Types Cartridge Fuse
The fuse is not interchangeable. The fuse base, adapter ring, cartridge and a fuse cap are the main element of the fuse. The cartridge is moved in the fuse cap. The cap is fixed on the fuse base. The tip of the fuse base is touch by the fuse element, and the circuit is completed through the fuse link.
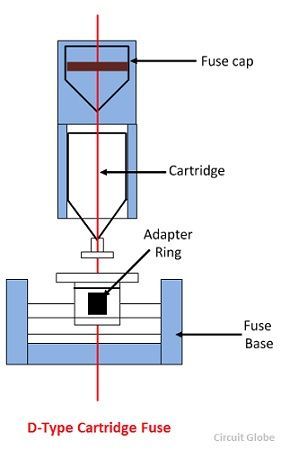 The standard rating of the fuse is 6, 16, 32, and 63 amperes. The breaking capacity of the fuse element is 4kA for 2 and 4 amperes fuses. The 16kA for 6 or 63 amperes fuses. This type of fuses does not have any disadvantages. The operation of the fuse is very reliable.
The standard rating of the fuse is 6, 16, 32, and 63 amperes. The breaking capacity of the fuse element is 4kA for 2 and 4 amperes fuses. The 16kA for 6 or 63 amperes fuses. This type of fuses does not have any disadvantages. The operation of the fuse is very reliable.
Link Type Cartridge or High Rupturing Capacity Fuses
The frame of the fuse is made of steatite. The steatite is the powder of the mineral. Mostly the ceramic material is used in the fuse because they had good mechanical strength. The brass cap holds the fuse element in the fuse. The brass caps are fixed on the ceramic body. It is fixed by using the special force so that the fuse can withstand high pressure.
The end contacts of the fuse are welded on the metallic cap. The powder of quartz is filled between the fuse element and the cartridge body of the fuse. This powder act as an arc extinguished medium in the fuse.
The powder of quartz absorbs the heat which induces because of the shortcircuit current. After absorbing the heat, the quartz is converted into the lead which opposes the restriking voltage.
The fuse element is made of silver or copper. It is linked by mean of the tin joint. The tin joint controls the temperature of the fuse from the short-circuiting current. The melting point of the silver is 980ºC while the melting point of tin is 240ºC. When the fault occurs in the system, the short-circuit current first passes through the tin. The tin prevents the shortcircuit current to flows through the silver.
The fusing factor of the link fuse is 1.45. The fusing factor of some special kind of fuses is 1.2. The knife blade and the bolted type are the types of fuses.

