In neutral grounding system, the neutral of the system or rotating system or transformer is connected to the ground. The neutral grounding is an important aspect of power system design because the performance of the system regarding short circuits, stability, protection, etc., is greatly affected by the condition of the neutral. A three phase system can be operated in two possible ways
- With ungrounded neutral
- With a grounded neutral
Ungrounded Neutral System
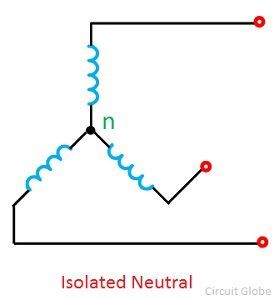
In an ungrounded neutral system, the neutral is not connected to the grounded. In other words, the neutral is isolated from the ground. Therefore, this system is also known the isolated neutral system or free neutral system shown in the figure below.
 Grounded System
Grounded System
In neutral grounding system, the neutral of the system is connected to the ground. Because of the problems associated with ungrounded neutral systems, the neutrals are grounded in most of the high-voltage systems.
 Some of the advantages of neutral grounding are as follows
Some of the advantages of neutral grounding are as follows
- Voltages of phases are limited to the line-to-ground voltages.
- Surge voltage due to arcing grounds is eliminated.
- The overvoltages due to lightning discharged to ground.
- It provides greater safety to personnel and equipment.
- It provides improved service reliability.
Method Of Neutral Grounding
The methods commonly used for grounding the system neutral are
- Solid grounding (or effective grounding)
- Resistance Grounding
- Reactance Grounding
- Peterson-coil grounding (or resonant groundings)
The selection of the type of grounding depends on the size of the unit, system voltage and protection scheme to be used.
