Definition: The overcurrent relay is defined as the relay, which operates only when the value of the current is greater than the relay setting time. It protects the equipment of the power system from the fault current.
Depending on the time of operation the overcurrent relay is categorized into following types.
- Instantaneous Overcurrent relay
- Inverse time Overcurrent Relay
- Definite Time Overcurrent Relay
- Inverse Definite Time Overcurrent Relay
- Very Inverse Definite Time Overcurrent Relay
- Extremely Inverse Definite Time Overcurrent Relay
- Instantaneous Overcurrent relay
Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
The relay has no intentional time delay for operation. The contacts of the relay are closed instantly when the current inside the relay rises beyond the operational value. The time interval between the instant pick-up value and the closing contacts of the relay is very less.
The most significant advantage of the instantaneous relay is that it has low operating time. It starts operating instantly when the value of current is more than the relay setting. This relay operates only when the impedance between the source and the relay is less than that provided in the section.
The most important feature of the relay is their speed of operation. The relay protects the system from earth fault and also used for protecting the system from circulating current. The instantaneous overcurrent relay is placed in the outgoing feeder.
Inverse-Time Overcurrent Relay
The relay operates only when the magnitude of their operating current is inversely proportional to the magnitude of the energize quantities. The operating time of relay decreases with the increases in the current. The operation of the relay depends on the magnitude of the current
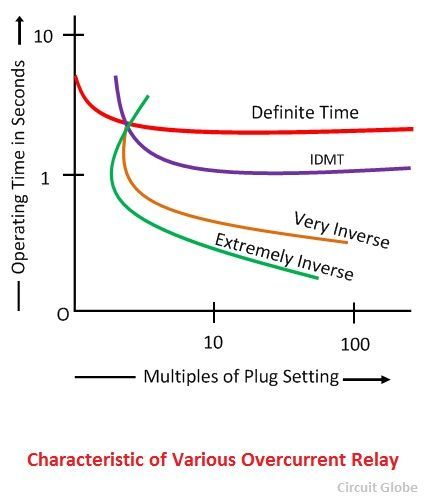
The characteristic curve for the relay is shown in the figure below. The relay will not operate when the value of current is less than the pick value. The relay is used for the protection of the distribution lines. The inverse time relay is of three types.
 Inverse Definite Minimum Time Relay
Inverse Definite Minimum Time Relay
The relay whose operating time is approximately proportional to the fault current is known as the IDMT relay. The operating time of the relay is maintained by adjusting the time delay setting. The IDMT relay uses the electromagnetic core because it can easily saturate for the current having larger magnitude than pick up current. The relay is used for the protection of the distribution line.
Very Inverse Relay
The inverse characteristic of the relay is more than the IDMT. Such type of relay is used in the feeder and on long transmission lines. The relay is used in the places where there the magnitude of the short-circuit current fall rapidly because of the large distance from the source. It is used for sensing the fault current which is free from the fault location.
Extremely Inverse Relay
The characteristic time of the relay is extremely large as compared to the IDMT and the Very inverse relay. This relay is used for protecting the cable, transformer, etc. The relay can operate instantly when the pickup value of the current is more than the relay setting time. The relay provides faster operation even under the fault current. It is used for sensing the overheating of the machines.
The inverse time relay is used in the distribution networks and the power plants. The relay gives the fast operation in the fault conditions because of their fault time characteristic.

Please, I need the definition of Directional overcurrent relay F67
HI All
i have small question ,
if extremely inverse curve is used , let say C3. why we program defnite time delay then ( 32ms for example ..)
many thanks for help