Definition: The motor which runs at synchronous speed is known as the synchronous motor. The synchronous speed is the constant speed at which the motor generates the electromotive force. The synchronous motor is used for converting the electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Construction of Synchronous Motor
The stator and the rotor are the two main parts of the synchronous motor. The stator becomes stationary, and it carries the armature winding of the motor. The armature winding is the main winding because of which the EMF induces in the motor. The rotator carry the field windings. The main field flux induces in the rotor. The rotor is designed in two ways, i.e., the salient pole rotor and the non-salient pole rotor.
The synchronous motor uses the salient pole rotor. The word salient means the poles of the rotor projected towards the armature windings. The rotor of the synchronous motor is made with the laminations of the steel. The laminations reduce the eddy current loss that occurs on the winding of the transformer. The salient pole rotor is mostly used for designing the medium and low-speed motor. For obtaining the high-speed cylindrical rotor is used in the motor.
Synchronous Motor Working
The stator and rotor are the two main parts of the synchronous motor. The stator is the stationary part, and the rotor is the rotating part of the machine. The three-phase AC supply is given to the stator of the motor.
The stator and rotor both are excited separately. The excitation is the process of inducing the magnetic field on the parts of the motor with the help of an electric current.
When the three-phase supply is given to the stator, the rotating magnetic field developed between the stator and rotor gap. The field having moving polarities is known as the rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field develops only in the polyphase system. Because of the rotating magnetic field, the north and south poles develop on the stator.
The rotor is excited by the DC supply. The DC supply induces the north and south poles on the rotor. As the DC supply remains constant, the flux induces on the rotor remains the same. Thus, the flux has fixed polarity. The north pole develops on one end of the rotor, and the south pole develops on another end.
The AC is sinusoidal. The polarity of the wave changes in every half cycle, i.e., the wave remains positive in the first half cycle and becomes negative in the second half cycle. The positive and negative half cycle of the wave develops the north and south poles on the stator respectively.
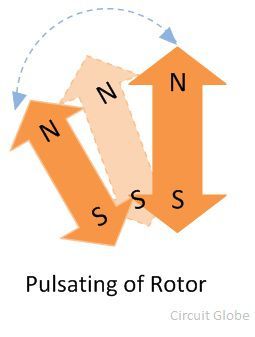
When the rotor and stator both have the same pole on the same side, they repel each other. If they have opposite poles, they attract each other. This can easily be understood with the help of the figure shown below: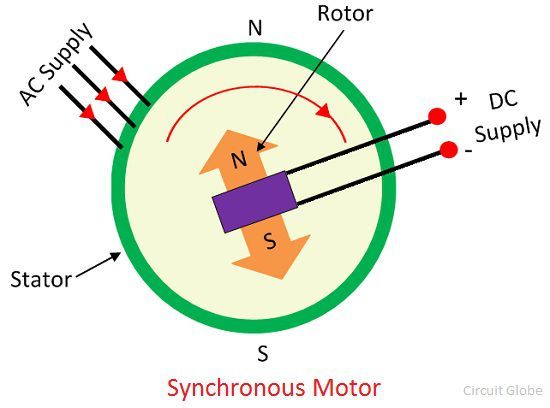 The rotor attracts towards the pole of the stator for the first half cycle of the supply and repels for the second half cycle. Thus the rotor becomes pulsated only at one place. This is the reason because of which the synchronous motor is not self-starting.
The rotor attracts towards the pole of the stator for the first half cycle of the supply and repels for the second half cycle. Thus the rotor becomes pulsated only at one place. This is the reason because of which the synchronous motor is not self-starting.
 The prime mover is used for rotating the motor. The prime mover rotates the rotor at its synchronous speed. The synchronous speed is the constant speed of the machine whose value depends on the frequency and the numbers of the pole of the machine.
The prime mover is used for rotating the motor. The prime mover rotates the rotor at its synchronous speed. The synchronous speed is the constant speed of the machine whose value depends on the frequency and the numbers of the pole of the machine.
When the rotor starts rotating at its synchronous speed, the prime mover is disconnected from the motor. And the DC supply is provided to the rotor because of which the north and south pole develops at their ends
The north and south poles of the rotor and the stator interlock each other. Thus, the rotor starts rotating at the speed of the rotating magnetic field. And the motor runs at a synchronous speed. The speed of the motor can only be changed by changing the frequency of the supply.
Main Features of Synchronous Motor
- The speed of the synchronous motor is independent of the load, i.e., the variation of the load does not affect the speed of the motor.
- The synchronous motor is not self-starting. The prime mover is used for rotating the motor at its synchronous speed.
- The synchronous motor operates both for leading and lagging power factor.
The synchronous motor can also be started with the help of the damper windings.

Why we construct circle diagram only for induction machine …? Why not synchronous machine?
Sir, I want to know about industrial application of the synchronous motors. In
which type of industry it is used. I have not seen them actually.
synchronous motors r normally used in power plants
because there is need of constant speed
Why rotor current is not induced in synchronous motor as in case of induction motor?
textile mills, hydro-electric station and every industry which requires constant speed used synchronous machines.
Explain what would happen when a centrifugal switch fails to open when a motor reaches about 75% of synchronous speed.