An Electromotive Force or EMF is said to be induced when the flux linking with a conductor or coil changes.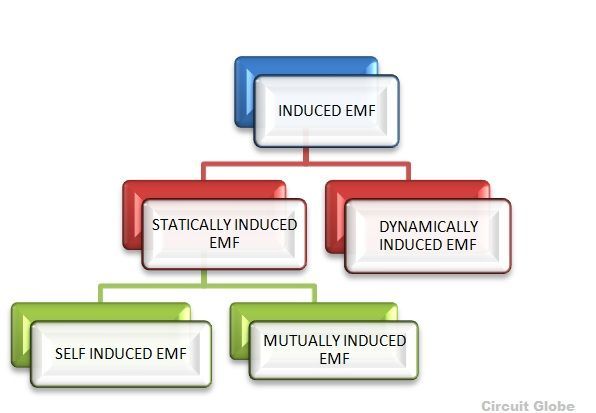
This change in flux can be obtained in two different ways; that is by statically or by dynamically induced emf. They are explained below
Contents:
1. STATICALLY INDUCED EMF
This type of EMF is generated by keeping the coil and the magnetic field system, stationary at the same time; that means the change in flux linking with the coil takes place without either moving the conductor (coil) or the field system.
This change of flux produced by the field system linking with the coil is obtained by changing the electric current in the field system.
It is further divided in two ways
- Self-induced electromotive force (emf which is induced in the coil due to the change of flux produced by it linking with its own turns.)
- Mutually induced electromotive force(emf which is induced in the coil due to the change of flux produced by another coil, linking with it.)
2. DYNAMICALLY INDUCED EMF
In dynamically induced electromotive force the magnetic field system is kept stationary, and the conductor is moving, or the magnetic field system is moving, and the conductor is stationary. Thus by following either of the two process the conductor cuts across the magnetic field and the emf is induced in the coil.
This phenomenon takes place in electric generators and back emf of motors and also in transformers.

better explanation than other sites