Definition: The number of magnetic lines of forces set up in a magnetic circuit is called Magnetic Flux. It is analogous to electric current, I in an electric circuit. Its SI unit is Weber (Wb) and its CGS unit is Maxwell. It is denoted by φm. The magnetic flux measures through flux meter. The fluxmeter has to measure coil which measures the variation of voltage to measure the flux.
Net number of lines passing through the surface are called magnetic lines of forces.

If the magnetic field is constant than the magnetic flux passing through a surface (S) is
![]() where
where
B – the magnitude of the magnetic field
S – area of surface
θ – angle between the magnetic field lines and perpendicular distance normal to the surface area
Magnetic flux for a closed surface
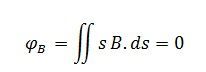
Magnetic flux for open surface
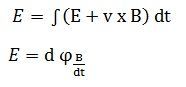 Where
Where
E – electromotive force
v – velocity of the boundary
E – electric field
B – magnetic field
øB – magnetic flux through the open surface
dl – infinitesimal vector element
The magnetic flux through a closed surface is always zero, but in the open surface, it is not zero.
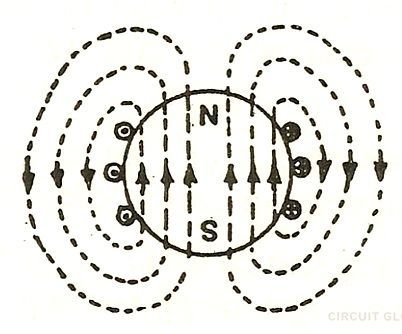
Properties of magnetic flux
- They always form a closed loop.
- They always start from the north pole and ends in the south pole.
- They never intersect each other.
- Magnetic lines of forces that are parallel to each other and are in the same direction repel each other.

It is very useful information that I got from you. Thank you very much
The information I got from your website is helpful and I would like to thank you..