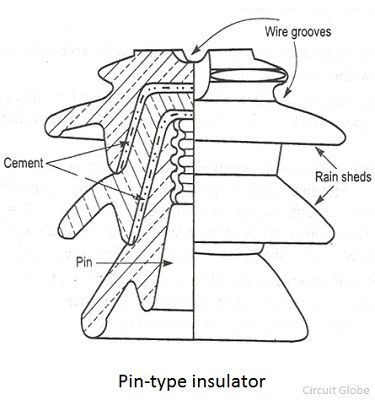
The pin insulator is used in power distribution for the voltage up to 33kV. It is placed on the cross arm of the supporting tower. The pin insulator has grooves on the upper end for keeping the conductor. The conductor is tied to the insulator on the top groove on straight line positions and side groove in angle positions by annealed binding wire of the same material as that of the conductor. A lead thimble is cemented into the insulator body to receive the pin.
The pin insulator uses non-conducting material like porcelain, ceramic, silicon rubber, polymer, etc., The weight of the polymer pin insulator material is more as compared to porcelain insulator material.
For low voltage, the single piece pin insulator is used, and for high voltage two or more pieces are cemented together for maintaining the proper thickness of the insulator. The insulator provides the adequate path to the leakage current.
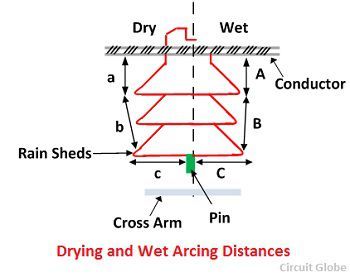
The flashover voltage for the moist and dirty surface is less than that for the clean and dry surfaces. The total dry arcing distance is the sum of all the direct distances through the air. It is represented by (a+b+c). The total wet arcing distance is (A+B+C).
Advantages of Pin Insulator
- It has high mechanical strength.
- The pin type insulator has good creepage distance.
- It is used on the high voltage distribution line.
- The construction of the pin type insulator is simple and requires less maintenance.
- It can be used vertically as well as horizontally.
Disadvantages of Pin Insulator
- It should be used with the spindle.
- It is only used in the distribution line.
- The voltage rating is limited, i.e., up to 36kV.
- The pin of the insulator damaged the insulator thread.
Causes of Insulator Failure
The electrical failure of insulator occurs either by puncture or flashover. In the case of a puncture, the arc passes through the body of the insulator. The flashover is caused due to the arc discharge between the conductor and the earth through air surrounding the insulator.
The flashover mainly occurs due to the line surge or due to the formation of wet conducting layer over the insulator surface. The insulator is not damaged by the flashover, but it’s become useless after the puncture.
The sufficient thickness of the material is provided in the insulator to prevent the puncture under surge condition. The flashover is reduced by increasing the resistance to leakage currents. The length of the leakage path is made large by constructing several layers called petticoats or rain sheds. The rain sheds kept the inner surface relatively dry in wet weather and thus provides sufficient leakage resistance to prevent a flashover.
The increased size, weight, and cost of pin insulator put a limit to its use above 66kV. Therefore the suspension insulators are used for high voltage work.

I enjoyed reading. Keep sharing more with us.
It’s good👍